Green manufacturing
· What is green manufacturing?
It is a manufacturing process in which use of minimal
natural resources, reducing pollution and waste, reuse and recycle the material
and lowering the emission in the process.
Fig 1. Green Manufacturing
· What is Additive manufacturing?
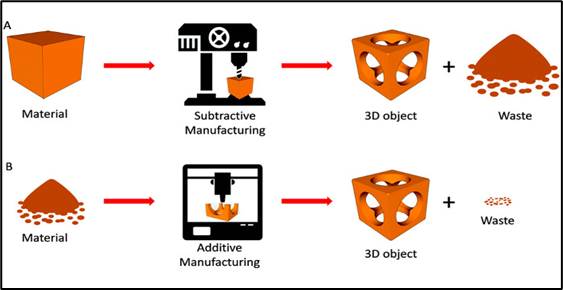
It is a process which is used for construction of a
three-dimensional geometry or objects from a CAD model by depositing materials
in layer-by-layer form. This process is opposite of subtractive manufacturing like
in which object is created by cutting away solid block until it formed.
Fig.2 Additive and Subtractive manufacturing
· Role of additive manufacturing in green manufacturing
Additive manufacturing is a process that saves the material resources as well as saves the energy which is used to generate that material. By using the additive manufacturing process the weight of an object is significantly reduced. Due to the less weight of the object the fuel consumption is also reduced. The additive manufacturing process does not require heavy transportation of the raw materials which is required in the conventional manufacturing processes and due to this additive manufacturing process reduces the emission of the harmful gases like carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide which are emitted by the vehicles during the transportation of raw material in the conventional machining processes which makes the additive manufacturing process more environmentally friendly.
Additive manufacturing process in food industry help
to reduce wastage of the food by avoiding the stocking the raw material in huge
amount which is not the case in the conventional process. By eliminating the
inventory, the amount of wastage is reduced in the additive manufacturing. In
the additive manufacturing the digitalization is a game changer as the additive
manufacturing requires CAD model to print the object and that CAD model can be
shared digitally and the object can be printed in the nearby locations or even
at home. The main purpose of the green manufacturing is to reduce wastage, to
lower the emission of the toxic gases that are harmful to the environment,
reuse and recycle the material and making the manufacturing process more
environmentally friendly these all purposes can be fulfilled by the additive
manufacturing process and that is the reason why additive manufacturing has a
crucial role in the green manufacturing technology.
Fig 3.AM towards environmental sustainability
· The ways that help 3d printing to go green
1) Designing more efficiently
By the use of 3d printing we can make the part shapes and features which are difficult or unachievable by other manufacturing process. The assemblies or the products that were made by using multiple parts now they can be made in one single piece and also in less time, material and labor work.
2) Less use of raw material
The 3d printing process uses less raw material and therefore the 3d printed material is light in weight and hence it is preferred to use in aircrafts, cars and it also benefits as it is more fuel efficient. The 3d printing process generate less wasted material than the other substrative manufacturing processes. Reducing the size of the print also helps in reducing the use of raw material.
Topology optimization is also a way to reduce use of
raw material and complex shapes can also be easily printed by the use of it.
Topology optimization is a mathematical approach that optimizes material layout
within a given design space for a given set of loads and
boundary condition such that the resulting layout meets a prescribed set of
performance targets. It senses that the design can achieve any shape within its
design space, instead of dealing with the predefined configuration.
3) Reduced emissions
The reduction in gases like carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide is possible because the design procedure is mainly carried out on computer and they can be shared digitally and we can print the parts in the nearest locations or even at homes so due to this there is decrement in the transportation which is required in conventional manufacturing processes, where there will be need of transportation is multiple times not only for the final product but also for the transportation of the raw material and shipping the material over long distance.
4) Eliminate the inventory
In the 3d printing process you can print small batches or print as per orders or demands there is no need of warehouse for spare and overstocking of the parts is not required. By these industries can save huge amount of money as we can manufacture the exact number of required parts. The main purpose is to eliminate inventory and use the material with considerably lower wastage. For ex: -Food waste reduction. Food waste can be reduced by 3d food printing and making the byproducts from it.
Ex: -KFC is working on to make the 3d printed chicken
nuggets and working on that with a Russian company named as 3d bioprinting
solutions to develop the technology that will print chicken meat using the
chicken cells
Fig4. Process of 3d bio-printed chicken
5) Reuse and recycling of the material
During the manufacturing processes there are many prototypes and iterations are made before making the ideal product design this results in unwanted item and faulty products and to avoid the wastage important raw material can be reused. So, the companies and industries are working on to use more sustainable raw materials to recycle the products.
For ex: - Some 3d printers use plastic bottles and
convert it into the raw material which can be reused.
Fig 5. Ways 3D printing helps go green
· Challenges faced in 3d printing while going for go
green approach
1) Energy consumption
The 3d printing technique reduce the energy consumption but some researchers hold the different opinion that the industrial grade printers use more energy than the injection molding machines. Research says that the 3d printers use 50 to 100 times more electrical energy than injection molding to make the object which are having same weight.
2) Negative environmental emission
Due to the characteristics of the several powders the negative environmental emission can be takes place in the 3d printing process. During the fused deposition modelling process the emission of the hazardous material takes place. During this 3d printing process using ABS and PLA cartridge will generate 1.61*1010 ea/min and 4.27 – 4.89*108 ea/min cartridge which are adversely affect the environment and human health this has been concluded in the paper named as “Emissions of nanoparticles and gaseous material from the 3d printer operation”.
3) Limitations of reusability of certain materials
In the 3d printing process the metal powder left from the print can be reused but there is a limitation on the number of times it can be reused to maintain its properties. In the high-tech industries or companies, the certain properties of the material and metal qualities are required there we cannot reuse the material and therefore it creates more scrap and waste.
· Conclusion:
In summary, the green manufacturing is essential part
of the sustainable development and gained importance recently. It entails using
eco-friendly procedures in every step of the manufacturing process, from
obtaining raw materials to getting rid of the waste. The green manufacturing
decreases the bad effect on surrounding and also provides businesses with
important benefits such as increase productivity, improves acceptability, reuse
and recycle of the materials.
· References:
1]https://www.azom.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=20017
3] https://images.app.goo.gl/YMG8SntXY2Sa22X69
4] https://youtu.be/ves5mclWXZ4
5] Kim, Yuna et al. “Emissions of Nanoparticles and
Gaseous Material from 3D Printer Operation.”
6] Liu, Zhichao, et al. "Sustainability of 3D
printing: A critical review and recommendations."
· Group Details: -
|
Name |
Roll No |
PRN No |
|
Darshan Behere |
62 |
12220228 |
|
Manswi Bhelkar |
63 |
12220023 |
|
Amey Bhombe |
64 |
12220239 |
|
Tushar Bhosale |
65 |
12220110 |
· Under the guidance of: -Prof. (Dr.) Ganesh G. Dongre





Nice job guys
ReplyDeleteGreat work 👍🏻
ReplyDeleteGood information
ReplyDeleteToday Industry really need the technology like green manufacturing and its very nice to see that you guys are making people aware of it.
ReplyDeleteNice information!
Good 👍
ReplyDeleteGood 👍
ReplyDeleteGreat blog!
ReplyDeleteGood job guys👍
ReplyDeleteWell done
ReplyDeleteVery good blog👌
ReplyDelete